In this work, the drag reduction by gas injection for power-law fluid flow in stratified and slug flow regimes has been studied. Experiments were conducted to measure the pressure gradient within air/CMC solutions in a horizontal Plexiglas pipe that had a diameter of 50 mm and a length of 30 m. The drag reduction ratio in stratified flow regime was predicted using the two-fluid model. The results showed that the drag reduction should occur over the large range of the liquid holdup when the flow behaviour index remained at the low value. Furthermore, for turbulent gas-laminar liquid stratified flow, the drag reduction by gas injection for Newtonian fluid was more effective than that for shear-shinning fluid, when the dimensionless liquid height remained in the area of high value. The pressure gradient model for a gas/Newtonian liquid slug flow was extended to liquids possessing the Ostwald-de Waele power law model. The proposed model was validated against 340 experimental data point over a wide range of operating conditions, fluid characteristics and pipe diameters. The dimensionless pressure drop predicted was well inside the 20% deviation region for most of the experimental data. These results substantiated the general validity of the model presented for gas/non-Newtonian two-phase slug flows.
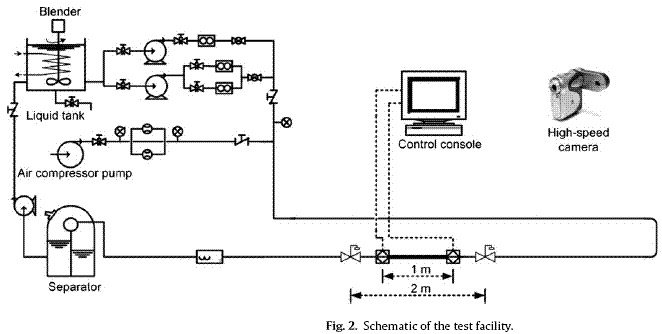
This paper was published as:
Xu JY, Wu YX, Li H, Guo J, Chang Y. Study of drag reduction by gas injection for power-law fluid flow in horizontal stratified and slug flow regimes. Chemical Engineering Journal,147(2-3):235-244(2009)

