- Home >> News >> Research Progress
Research Progress
Phononic thermal properties of two-dimensional materials
Thermal conductivity is used as a indicator for the heat conducting capability of a material. The validity of the Fourier’s law of heat conduction in low-dimensional materials has been challenged in recent decades. In a recent review article published in the Reviews of Modern Physics, the coauthors from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Colorado at Boulder presented the latest theoretical advances in phononic thermal properties of two-dimensional materials.
From the phonon scattering picture, the authors first summarized and compared the phonon properties, such as phonon dispersion and relaxation time, of pristine 2-D materials with single layer graphene to understand the role of crystal structure and dimension on thermal conductivity. They then compared the phonon properties, contrasting idealized 2-D crystals, realistic 2-D crystals, and 3-D crystals, and synthesizing this to develop a physical picture of how the sample size of 2-D materials affects their thermal conductivity. The effects of geometry, such as number of layers, and nanoribbon width, together with the presence of defects, mechanical strain, and substrate interactions, on the thermal properties of 2-D materials were discussed. A discussion of the challenges in theoretical and experimental studies of thermal transport in 2-D materials was also supplied. The paper is of importance to guide the synthesis and design of low-dimensional functional materials with excellent thermal-mechanical-electrical coupled properties.
The co-author, Yujie Wei, would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant no. 11425211), and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB22020200).
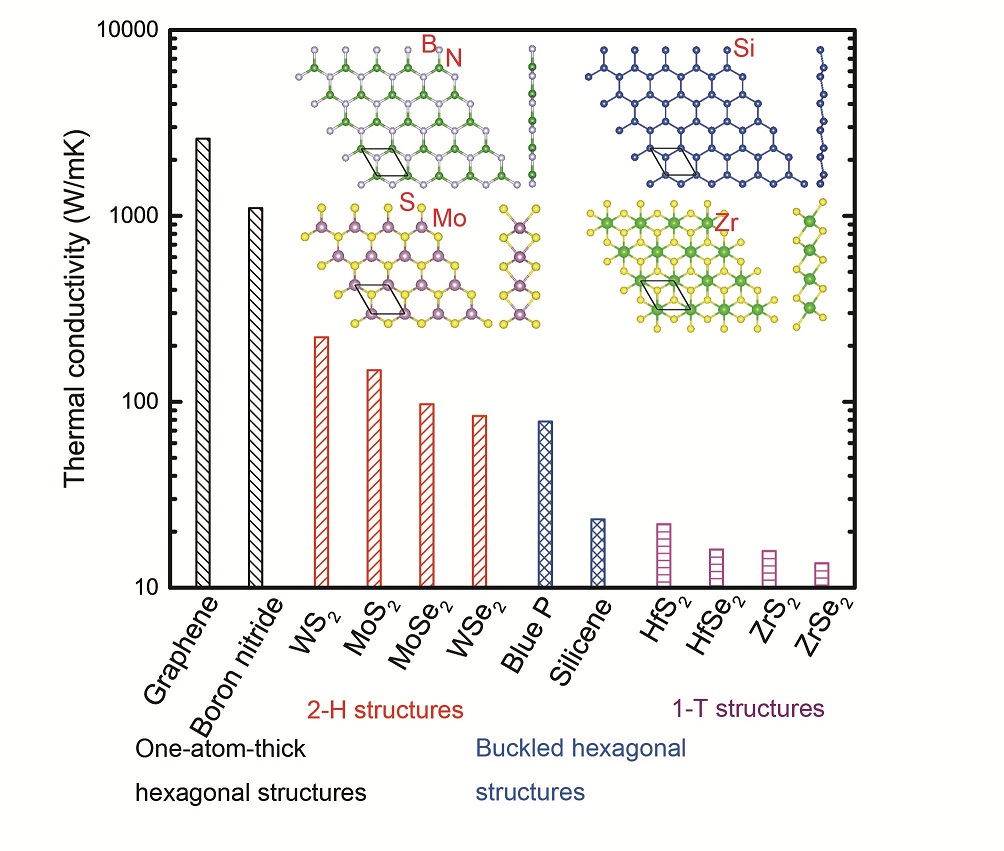
Figure: Thermal conductivities of some typical single-layer 2-D materials at room temperature. The data are sorted by descending thermal conductivity values. Inset: the atomic structures of boron nitride, silicene, MoS2, and ZrS2 as examples of 2-D materials with different crystal structures.
Xiaokun Gu, Yujie Wei, Xiaobo Yin, Baowen Li, Ronggui Yang, Colloquium: Phononic thermal properties of two-dimensional materials, Rev. Mod. Phys., 90, 041002 (2018)
Link: https://journals.aps.org/rmp/abstract/10.1103/RevModPhys.90.041002